As AI adoption continues to rise, so does the prevalence of shadow AI, or unapproved usage of AI.
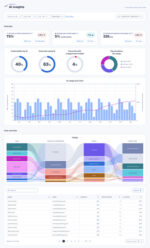
In a new survey from ManageEngine, 60% of the 700 survey respondents admitted to using unapproved AI tools and 93% admitted to adding information to AI tools without approval.
32% of employees entered confidential client data into an AI tool and 37% entered private company data.
The top tasks employees use unauthorized AI for are summarizing notes or calls (55% of respondents), brainstorming (55%), and analyzing data or reports (47%). The types of AI tools most commonly approved for employee use by IT teams are generative AI text tools (73%), AI writing tools (60%), and code assistants (59%).
ManageEngine believes that a lack of education around AI model training, safe user behavior, and organizational impact is leading to more shadow AI.
Additionally, 85% of IT decision makers admitted that employees are adopting tools at a pace that is faster than the IT teams can assess them.
Another issue compounding the problem is that only 54% of respondents said that their organizations have clear AI governance policies in place and actively monitor for unauthorized use.
Some recommendations from IT decision makers on how to curb shadow AI include integrating approved tools into standard workflows and applications, implementing clear policies on acceptable use, and establishing a list of vetted and approved tools.
From the employee perspective, some recommendations are to have IT set clear policies that are fair and practical, provide official tools relevant to their jobs, and provide better education on risks.
“Proactive AI management unites IT and business professionals in their pursuit of common, organizational goals. That means employees are equipped to understand and avoid AI-related risks, and IT is empowered to help them use AI in ways that drive real business outcomes,” said Sathish Sagayaraj Joseph, regional technical head at ManageEngine.